The project
The Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) is funding the WEISS_4PN project within the WAVE funding measure as part of the federal research program on water “Wasser: N”. Wasser: N contributes to the BMBF “Research for Sustainability (FONA) Strategy”
WEISS_4PN: Integrative application of innovations and digital cooling capacity management to reduce the amount of water required in steel production
Project term: 01.04.2021-31.10.2024
Funding code: 02WV1570A
Partners


Objective
- Ensuring water availability
- Application of innovative technologie
- Tapping the full potential of digitalization
- Transferability to other facilities, incl. concentrate treatment
- Sustainability in concentrate treatment
- Establishment of a reference project

Overview
In the industrial sector, water is mainly needed for cooling. In the steel industry, 75% of the amount of water used is required for cooling. Facing climate change, it must be assumed that the availability of water will – at least temporarily – be limited in the future. In order to nevertheless ensure high operational reliability for steel production, the demand for fresh water must be largely separated from production operations and minimized by recovering water from the production site's wastewater.

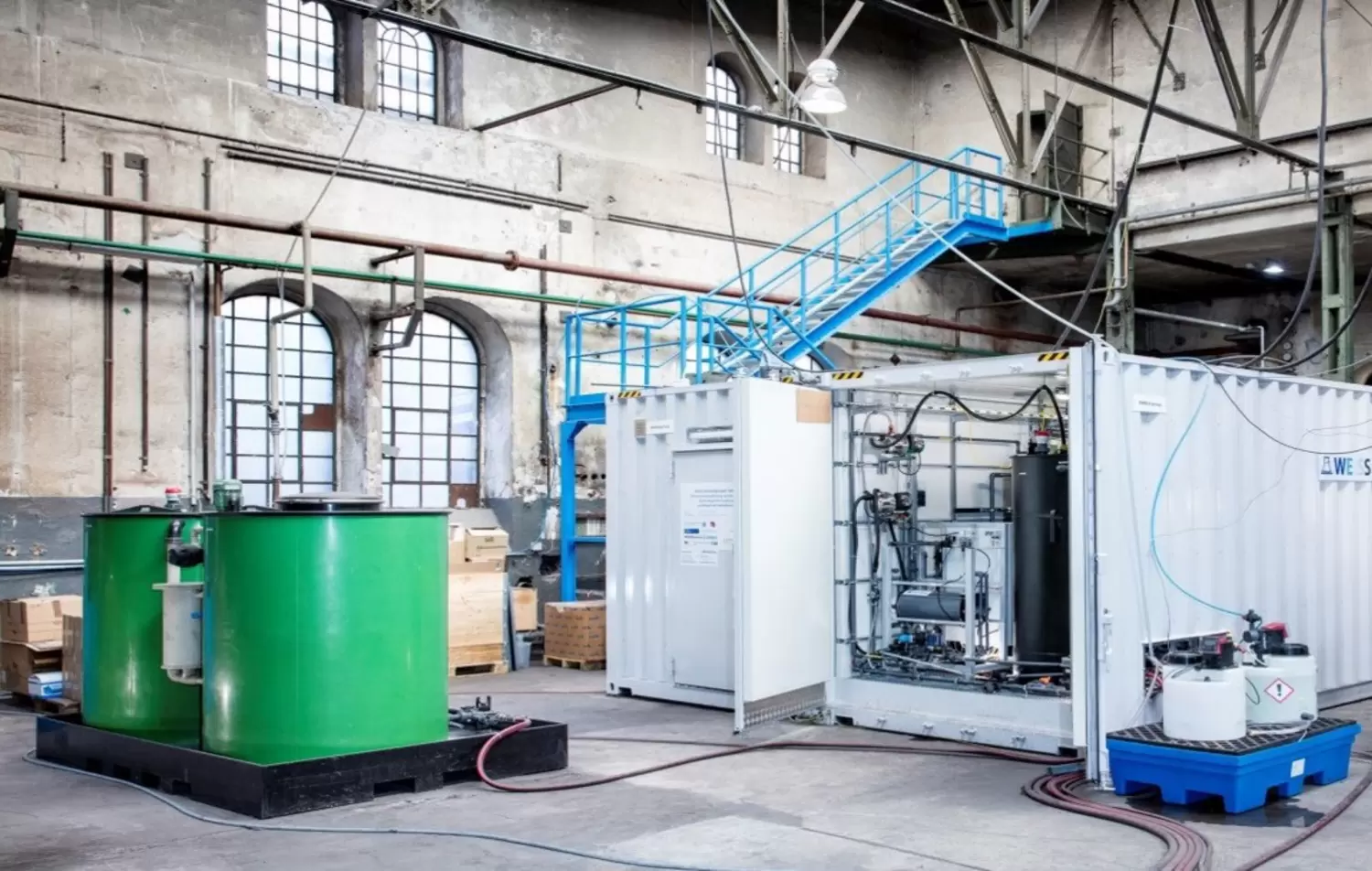
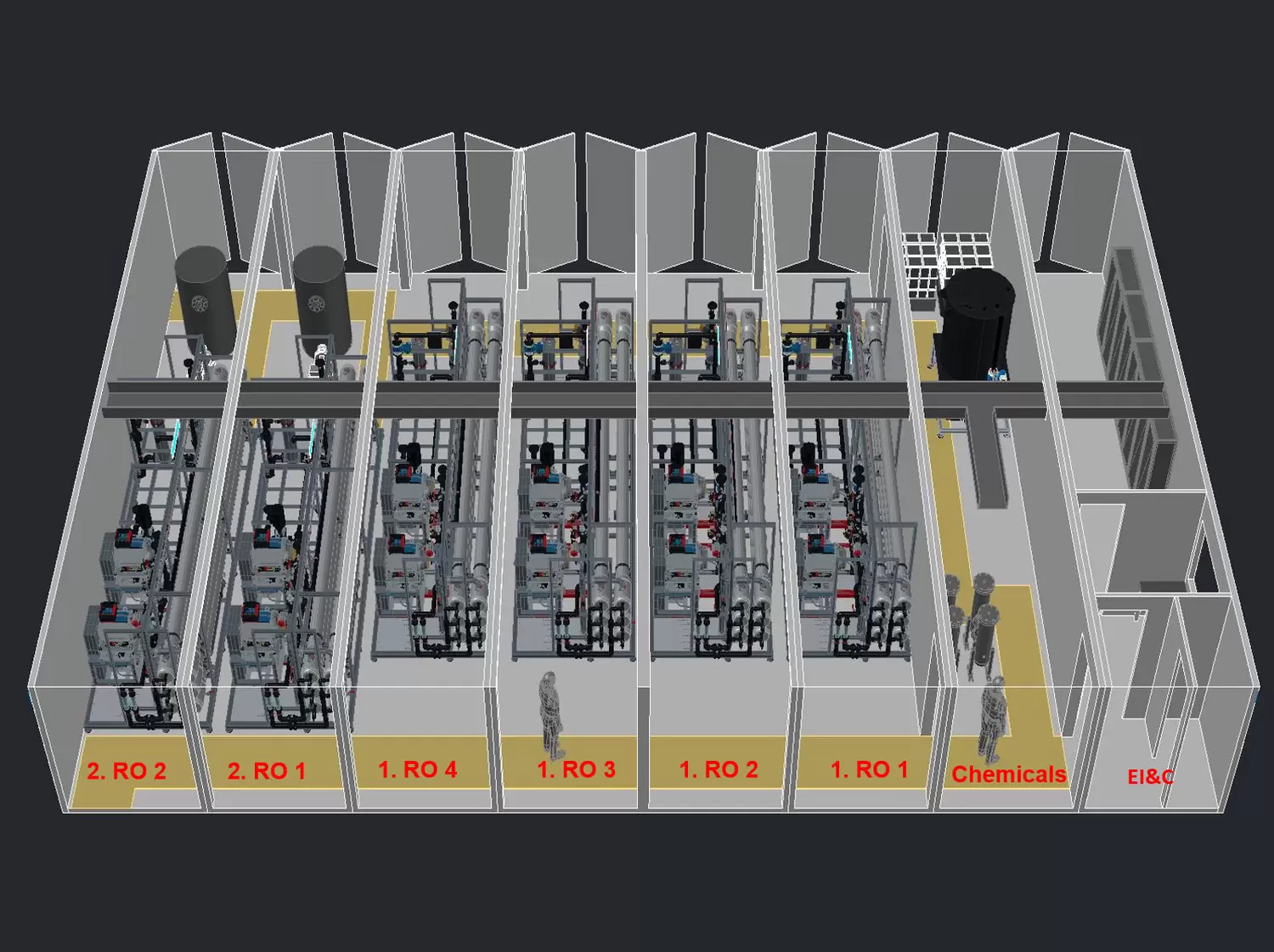
For this purpose, the pilot plant (capacity: 1 m³/h) available from the WEISS project will be set up at the Eisenhüttenstadt facility and waste water volumes that had not been considered to date will be desalinated so as to make maximum use of the potential to compensate for evaporation losses occurring in open cooling circuits using in-house water flows. First of all, the discharge of the waste water treatment system will be tested. For this purpose, after thorough analysis of the water composition, additionally required pre-treatment steps will be defined and their effectiveness will be tested in the laboratory. The pre-treatment tested in this way will then be implemented and integrated in the pilot plant, and the waste water will be desalinated.
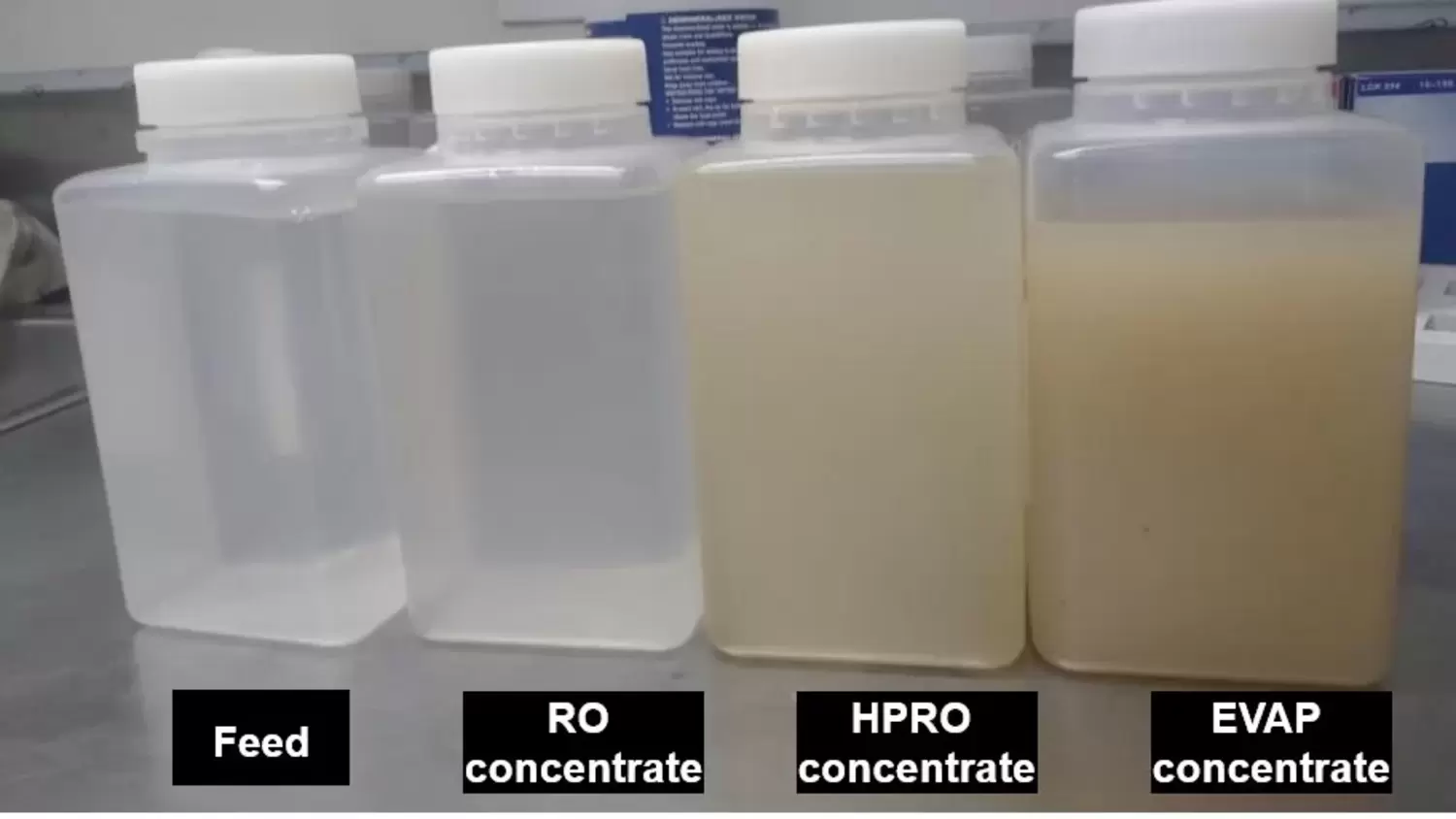

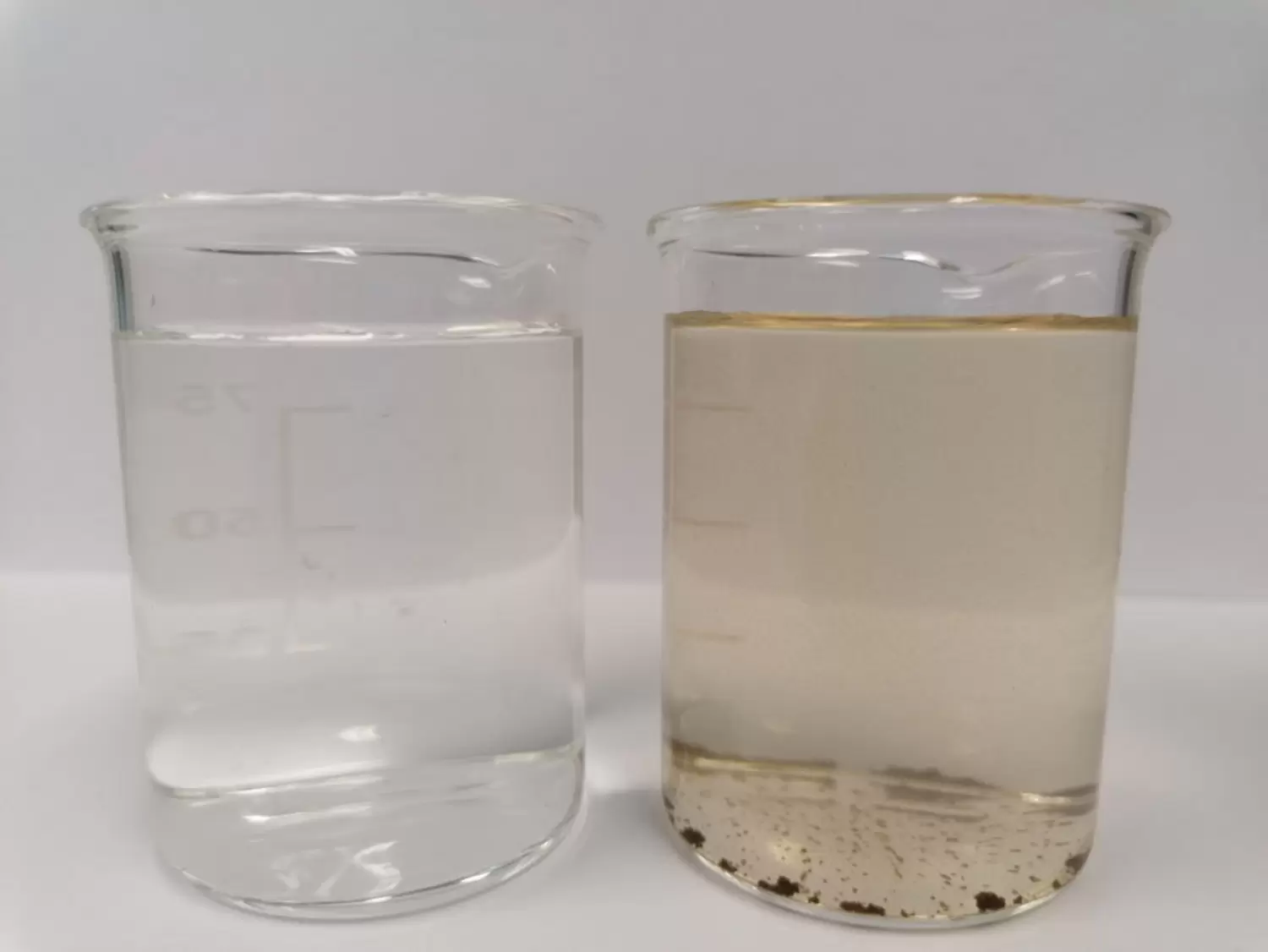
A crucial aspect for the economic application of this concept is the safe and cost-effective disposal of the concentrates produced in the desalination process. That is why the salt fractions will be separated from each other by means of two different approaches.
An optimization and forecasting tool is intended to determine the development of the composition and the availability of fresh water to be able to detect bottlenecks at an early stage. A digital cooling capacity management system integrated in the process is intended to optimally utilize the potential of the existing cooling circuit systems by linking the production-related heat load with the current weather-related cooling capacity. Finally, the concepts shall be evaluated economically and ecologically in order to select the most economically favorable and environmentally compatible solutions.

-
Laboratory testing
- TUB + BFI | Concentrate treatment
- WEHRLE | Pre-treatment of waste water for reverse osmosis (RO)
- UDE | Acid-resistant antifouling membranes
- BFI | Membrane capacitive deionization (mCDI)
![]()
-
Pilot tests
- WEHRLE + SMS | Pre-treatment and 2-stage desalination of waste water
- WEHRLE | Integration of pre-treatment into the pilot plant
- WEHRLE | Desalination of waste water
![]()
-
Theoretical considerations
- SMS | Concept preparation
- SMS | Cost comparison Multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA)
- TUB | Life cycle assessment (LCA)
![]()
-
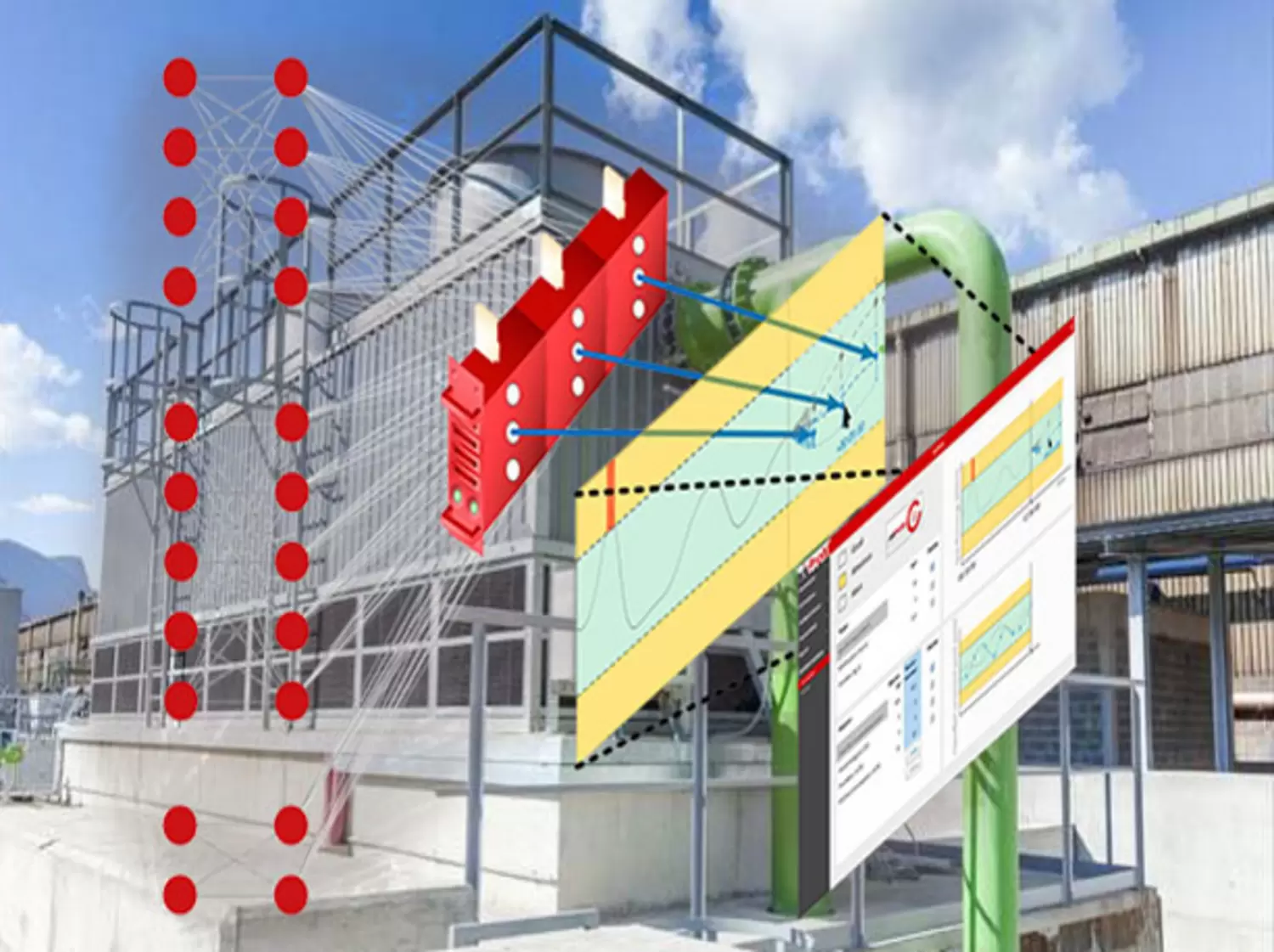
Digitalization
- AIXPROCESS + SMS | Digital cooling capacity management
- BFI | Digital forecasting tool
![]()
Contact
-
Stefan Schmidt
-
Stefan Schmidt
Manager Fluid & Piping Systems
![]()
Sponsored by

Networking and transfer projects coordinated by